Judiciary CLAT Notes: What are the Fundamental Rights of Indian Citizens?
Judiciary CLAT Notes: Fundamental Rights are one of the important features of the Indian Constitution. These are some of the special rights given by the Constitution to the citizens of India.
Fundamental Rights are one of the important features of the Indian Constitution. These are some of the special rights given by the Constitution to the citizens of India that were acquired from the Constitution of independent India. The courts of India play an important role in the case of violation of fundamental rights.
The main objective of the Fundamental Rights is to give Indian citizens the right to a free, equitable, just, secure and fulfilling life with rights. The Fundamental Rights are mentioned in the Preamble of the Constitution which states that the Constitution ensures the rights which are necessary for the creation of a just and equitable society.
Fundamental Right
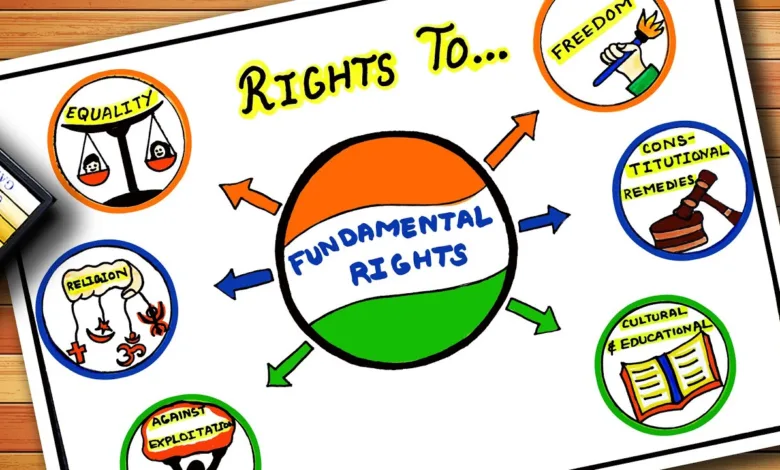
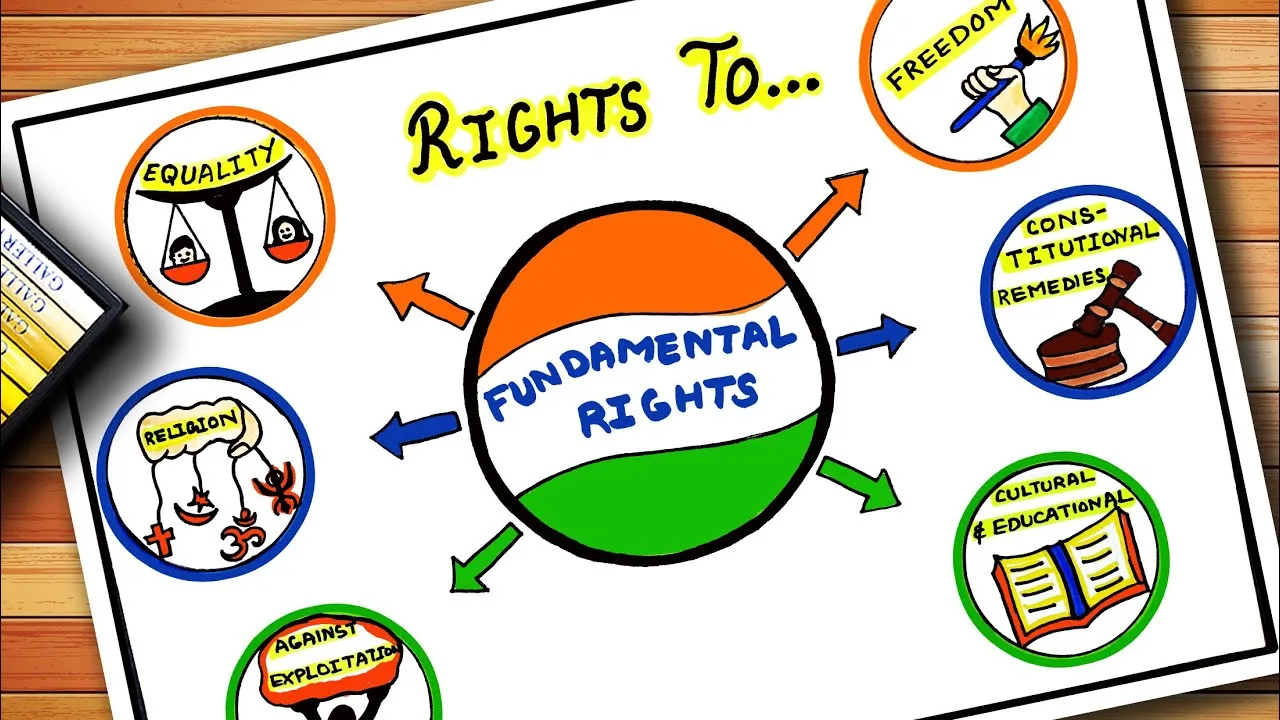
Fundamental Rights include the following rights:
The most important and fundamental aspect of human rights is the dignity and protection of various rights, which are established in the Indian Constitution. The constitutional proof of these rights is given in various articles of the Constitution. This includes the right to equality, the right to freedom, the right against exploitation, the right to religious freedom, the right to culture and educational rights, and the right to constitutional remedies.
Right to equality:
This right is available in detail from Articles 14 to 18. It includes the right of Indian citizens to have equal and human status, personal liberty, protection against discrimination on the basis of caste, religion, sex, birth, etc., the right to equal pay, and the right to access common places.
Right to freedom:
This right is guaranteed by Articles 19 to 22 and includes the right to freedom such as personal liberty, right to speech, religion, formation of association and insertion into the union, prohibition of detention against unlawful delay, free religious propagation and protection against exploitation.
Right against exploitation :
This right is detailed in Articles 23 to 24 and includes the right to protection against child labour, commercial and exploitation of regular workers.
| Join Telegram Group | Click Here |
| Join WhATSAPP channel Agra University | Click Here |
Right to religious freedom:
This right is provided by Articles 25 to 28 and includes the right to individual religious enhancement, adherence to religious ideals and universal equality.
Culture and Educational Rights
This right is available from Articles 29 to 30 and includes the appreciation of culture, the protection of minority communities, and the right to education of citizens.
Right to constitutional remedies
This right comes in detail from Articles 32 to 35 and includes the right to constitutional remedies, the right to share, the right to authority and the right to liability of the authorities.
In addition to these rights, some other general rights are also available to the citizens which are as follows:-
Right to Life, Health and Occupation: Under this right, every person has the right to run his life, health and business freely.
Right to Justice: Under this right, every person has the right to go to court and get his case heard according to the just ideology.
Property Rights: Under this right, every person has the right to use his property according to his choice and become its owner.




One Comment